Cycle Time in Azure DevOps
🤔 Context: A project manager needs to measure the efficiency of their team’s workflow by calculating Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) such as Cycle Time. These metrics are crucial for assessing the balance between productive work and waiting periods throughout the project's lifecycle.
🌧️ User Problem: As a project manager, I need to accurately calculate the efficiency of our project by measuring Cycle Time. This helps me understand the time spent actively working on tasks versus the time tasks spend waiting, ensuring that our processes are optimized and project goals are met effectively.
☔ Solution: Using the Time in State, you can efficiently calculate both Cycle Time to determine your project’s efficiency.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are widely adopted metrics to assess the effectiveness of practices, products, projects, or initiatives. In project planning, KPIs are meticulously defined to gauge performance, beginning from day zero and tracked throughout every stage. Initiating a project with a well-defined objective requires a systematic measurement of effectiveness and the accuracy of steps taken toward the goal. KPIs play a crucial role in providing concrete insights into decision-making, reinforcing their validity, and evaluating the overall quality of ongoing efforts.
Indicator Efficiency can be defined as the balance between Cycle Time. These metrics are interconnected with the duration it takes to develop a feature and the time spent waiting before deploying it in production.
To calculate Efficiency, you first need to calculate two indicators - Wait and Cycle Time.
Cycle Time
Cycle Time = sum working time by closed items per period in a particular state.
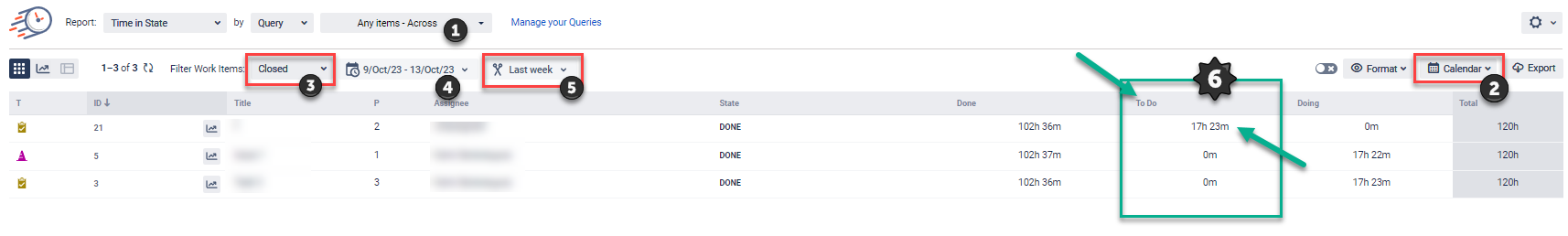
Follow this guide to calculate Cycle Time using Time in State extension:
Select a query for the report generation.
Select a calendar for the correct calculation.
Filter Work Items by Closed.
(Optionally) Select the item’s range in the “Work Item“ dropdown (to display items closed in such period).
Select a period in the “Time range” dropdown (to display the time calculation for the selected item range in the specific time range).
Look at the State column, and the time that item was in such an active state (for example Doing, Active, etc).
If you need help or want to ask questions, please contact SaaSJet Support or email us at support@saasjet.atlassian.net
Haven't used this add-on yet? Try it now >>>Time in State for Azure DevOps